ADUs have gained immense popularity in recent years. As the price of real estate skyrockets, homeowners are switching to ADUs.
This helps them utilize the existing space and get additional income. They are accepted as a viable solution to various housing challenges.
Common reasons for this are the need for affordable housing options, multi-generational living arrangements, and also a source for homeowners’ supplemental rental income.
If you have questions like:
What are ADUs in Real Estate?
How much does it cost to build an ADU?
Does ADU increase home value?
Then you’ll find this guide useful, as we try to provide you with an understanding of ADUs, including their types, pros, and cons.
What to Expect?
- Reasons for the rising popularity of ADUs
- Types of ADUs and how to choose them
- Finalizing the design and construction of your ADU
- Navigate various financing and investment options for ADUs
- Pros and cons of ADUs
- Future trends and outlook in the ADU space
Understanding Accessory Dwelling Units a.k.a. ADUs

Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) are sometimes also called granny flats, in-law units, or secondary suites. These dwelling units are self-contained living spaces that are either attached to or detached from a primary residence.
To qualify as an ADU, it must be equipped with a kitchen, bathroom, and sleeping area. These help to provide the occupants with a sense of independence, while still being on the same property as the main house.
Find more about the role of ADUs in alleviating America's housing shortage.
ADUs are a versatile and cost-effective way to maximize the use of your existing residential properties without the need for a large-scale development project.
These are the various types of ADUs and their advantages and disadvantages:
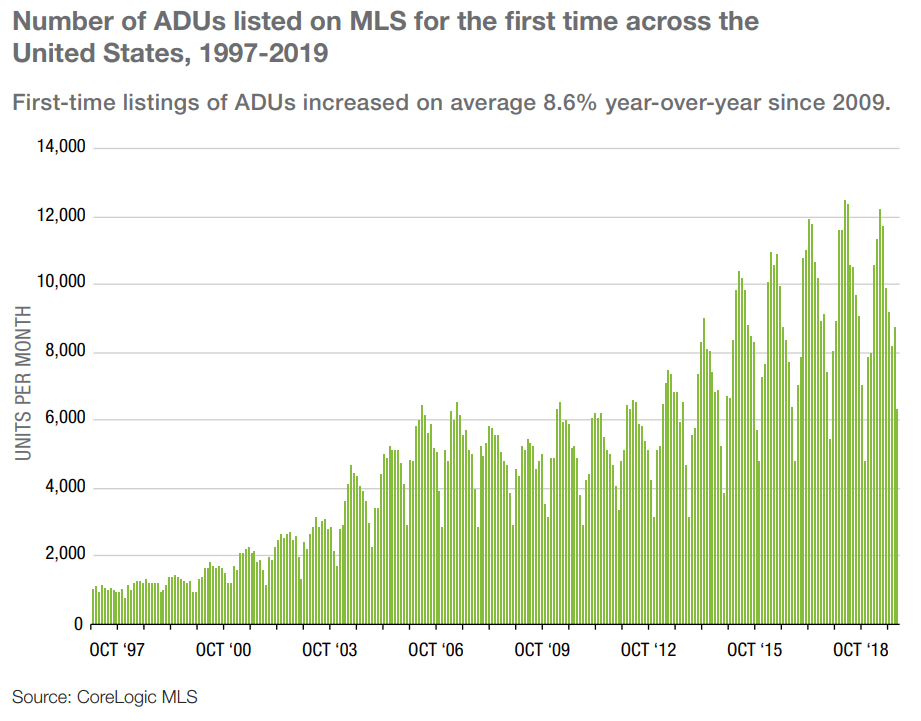
Types of ADUs
These are the common types of ADUs in the U.S. You can select the ADU type based on the size and architecture of your property or your requirements.
1. Attached ADUs

Attached ADUs are the most common and popular type of attached dwelling. They are connected to the primary residence, often sharing a wall or a portion of the existing structure. They can be a basement apartment, an attic conversion, or an extension of the main house. Attached ADUs offer convenience and accessibility for occupants, as they are typically located close to the main living areas of the house.
Advantages of Attached ADUs
- Offer convenient access to the main house amenities
- They are more cost-effective to construct, compared to detached units
- Usually need less extensive permitting and zoning approvals
- Integration with existing infrastructure means lower construction costs
Disadvantages of Attached ADUs
- Offer limited privacy, when compared to detached units
- Noise transfer between the main house and the ADU
- Restrictions on expansion or modifications as they are attached to the main structure
- Limited flexibility in layout and design because of existing building constraints
2. Detached ADUs

These are primarily standalone structures, which are separate from the primary residence. You can get them built in the backyard, over a garage, or as a separate cottage on your property. Detached ADUs offer increased privacy for both you and the occupant. Their separation from the main house makes them ideal for rental units or as living spaces for the members of your extended family.
Advantages of Detached ADUs
- Offer maximum privacy and separation from the main house
- Their flexibility in design and layout allows customizations based on specific needs
- There is reduced noise transfer between the main house and the ADU
- They have a higher rental income potential due to the standalone nature of the unit
Disadvantages of Detached ADUs
- They have a higher construction cost compared to attached or conversion units
- These units require additional space on the property for construction
- There may be stringent permitting and zoning requirements, especially in densely populated areas
- They require separate maintenance and management because of their separation from the main house
3. Conversion ADUs
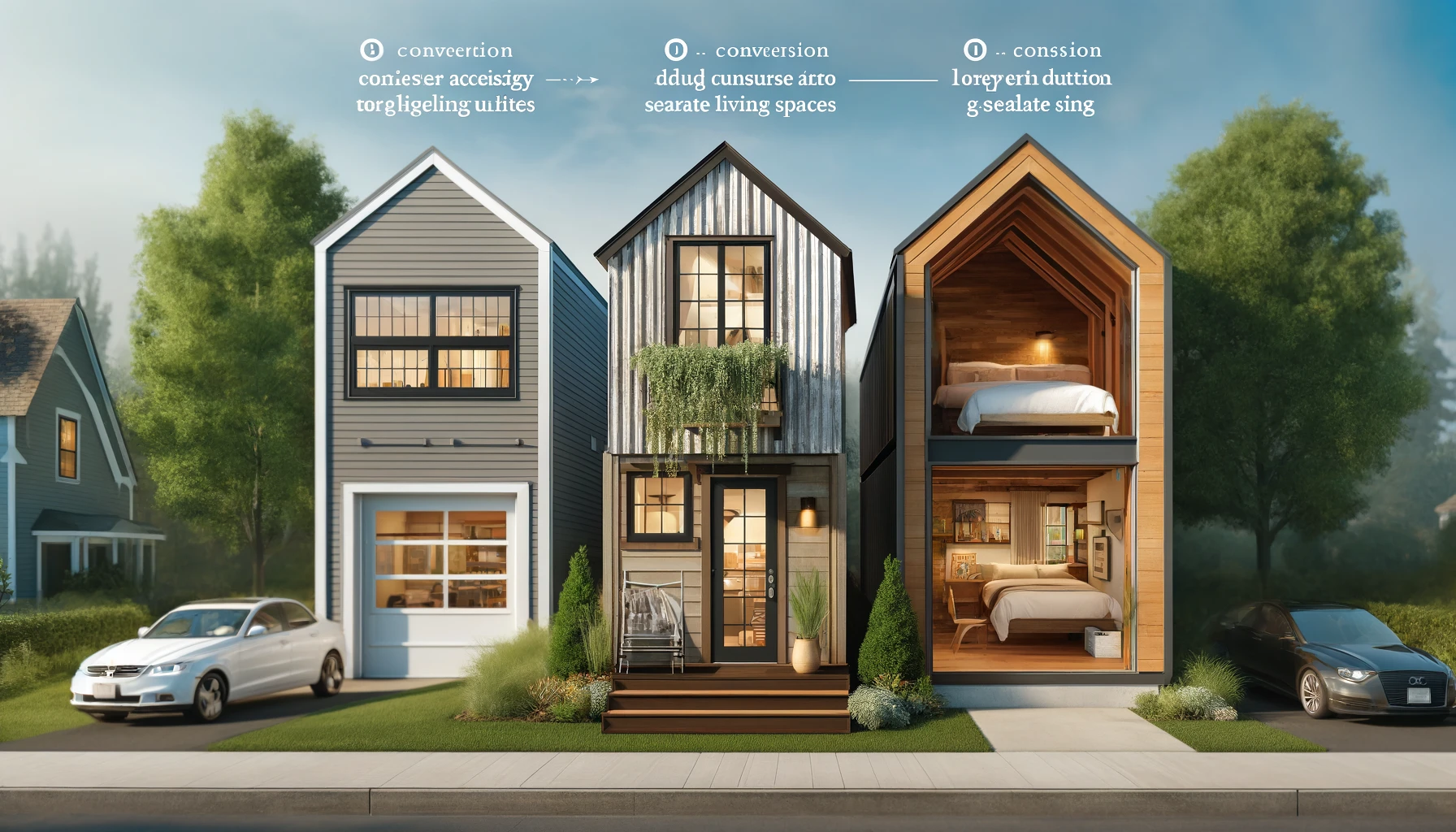

These types of units are built by repurposing the existing structures on the property. Common examples are a garage, shed, or even a portion of the main house. These are repurposed into a separate living unit. Conversion ADUs are more cost-effective than building new structures from scratch. The reason is that they mostly utilize existing infrastructure and usually require less extensive construction work.
Advantages of Conversion ADUs
- These units utilize existing structures on the property and do not require new construction
- They are more cost-effective compared to building new structures
- Such units have a faster construction timeline in comparison to other ADUs
- They add value to underutilized or unused spaces on your property
Disadvantages of Conversion ADUs
- The units are limited by the size and condition of the existing structure
- The existing structure may require costly renovations or repairs
- You may face challenges with permitting and zoning regulations
- Difficulty with approvals if the structure is not originally intended for residential use
- Design limitations and less flexibility, when compared to new construction
- Customization limitations, compared to purpose-built ADUs
ADU Design and Construction

The design and construction of Accessory Dwelling Units require careful review of various aspects. You must consider factors that will help to ensure a functional and aesthetically pleasing living space.
When it comes to ADUs, maximizing space and functionality is essential, with efficient floor plans, multi-functional furniture, and ample natural light.
Consider consulting with professionals such as Architects, Designers, and ADU investment advisors. They can provide you with valuable guidance throughout the design and construction process.
Factors Influencing Design and Construction
There are several factors that you need to consider, when planning the design and construction of an ADU, such as:
- Size and layout of the property
- Local building codes and regulations
- Existing infrastructure
- Budget constraints
These all factors influence the design and construction process. Consider working with an experienced architect or designer. Such an expert can help you create a functional and aesthetically pleasing ADU that meets your needs and complies with local regulations.
Considerations for Maximizing Space and Functionality
Efficient use of space is essential when designing an ADU. This includes floor plans, multi-functional furniture, and maximizing natural light, to create a comfortable living environment. Also, plan for accessibility features for occupants with mobility challenges.
Permitting and Zoning Regulations
Before starting ADU construction at your property, it's crucial to familiarize yourself with local permitting and zoning regulations. These can vary significantly from one jurisdiction and state to another. It may impact the size, location, and design of your ADU.
Consider hiring a knowledgeable contractor or ADU investment advisor for your project. An experienced professional can help ensure that your project complies with all applicable regulations and you get all the necessary approvals. They can also provide valuable insights tailored to your specific situation and location.
Financing and Investment Considerations

Another important aspect of ADU construction is related to finance and investment for the project. The construction of an Accessory Dwelling Unit is not cheap, and there might of unplanned expenditure at any stage. You need both planned expenditure outlay along with a financial cushion to deal with cost escalation.
Cost of Building an ADU
The cost of building an ADU can vary and depends on various factors, such as:
- Size of the Unit
- Design Complexity
- Choice of Materials
- Labor Costs
It's essential that you budget carefully and get accurate cost estimates before starting with the construction. ADUs require a significant upfront investment that you need to bear or get financed. However, in the long term, they can also provide a steady stream of rental income for you. They can also potentially increase the overall value of your property over time.
Financing Options for ADU Construction
You can finance the ADU project at your property through various methods, such as:
- Cash Reserves
- Home Equity Loans
- Construction Loans
- ADU-specific Financing Programs
Each of these options has its pros and cons. It is essential to explore all available options and choose the one that best fits your financial situation and long-term goals.
ROI Potential

ROI is a crucial consideration for every investor. To calculate the return on investment (ROI) for an ADU you need to consider various factors such as:
- Rental Rates Of Similar Units
- Vacancy Rates In Your Location
- Likely Property Appreciation
- Regular Maintenance Costs of the ADU
The rental income from your ADU can provide a steady source of cash flow. It is, however, essential to factor in all associated expenses. Only then can you realistically evaluate the potential risks and rewards of ADU ownership.
Consulting with an ADU investment advisor can help you develop a comprehensive investment strategy. But be sure that take into account your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
You can also check HUD’s comprehensive report with valuable insights into the financial aspects of ADU construction, including cost breakdowns, financing strategies, and return on investment analyses.
Pros and Cons of ADUs
ADUs offer several benefits, but they also come with their own set of challenges. Consider them carefully before you make an informed decision.
Pros
Additional Rental Income Potential
ADUs can generate rental income that can help offset mortgage payments, property taxes, and other expenses associated with homeownership.
Increased property value
Adding an ADU to your property can increase its overall value. It will also make it more attractive to potential buyers.
Flexibility for Multi-Generational Living Arrangements
ADUs provide a separate living space for family members, such as ageing parents or adult children, while still allowing them to remain close by.
Potential Tax Benefits
As a property owner, you may be eligible for tax incentives or deductions related to ADU ownership. Examples of this are property tax exemptions or depreciation deductions. However, please note that these are dependent on local tax laws and regulations.
Cons
Upfront Construction Costs
Building an ADU can require a significant upfront investment. For example, construction costs, permitting fees, architectural expenses etc.
Potential Permitting and Zoning Challenges
Navigating the permitting and zoning process for ADU construction can be complex and time-consuming. Your areas may have strict regulations or limited housing supply.
Ongoing Maintenance
As the property owner, you are responsible for maintaining the ADU. You may also need to address tenant issues and ensure compliance with local rental laws and regulations.
Impacts on Property Taxes and Insurance Premiums
Adding an ADU to a property may increase your property tax burden and insurance premiums. However, the extent of this depends on various factors such as the size and value of the ADU and local tax laws.
Future Trends and Outlook
The popularity of ADUs in real estate is expected to continue growing in the coming years. Here are some pointers in this direction:
Growing Popularity of ADUs in Real Estate
Housing affordability remains a significant concern in many urban areas. ADUs offer a cost-effective solution for adding much-needed housing supply. They can easily infill development in established neighbourhoods.
According to a study by the Urban Institute, Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) have emerged as viable housing options across the U.S.
Potential Changes in Regulations and Policies
As the demand for ADUs increases, policymakers may enact changes to zoning laws, building codes, and financing options. This will help to boost construction and streamline the approval process. Some cities and municipalities are already implementing ADU-friendly policies. Examples of this are waiving permitting fees or providing financial incentives for ADU construction.
AHURI's final report provides valuable insights into the impact of regulatory changes on Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs).
Emerging Innovations in ADU Design and Construction
Advances in construction technology, sustainable building practices, and modular construction methods are popularising ADUs. They are driving innovation in design and construction, making these units more affordable, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
New design trends, such as tiny homes and accessory dwelling modules (ADMs), have also become popular. They offer homeowners a wide range of options for customizing their ADU to suit their needs and preferences.
Conclusion
ADUs represent a unique opportunity for property owners and investors to unlock the full potential of their properties. This is done by adding additional living space and potential rental income. However, investing in an ADU requires careful planning, financial analysis, and consideration of local regulations and market conditions.
Consulting with an ADU investment advisor or financial advisor can help you navigate the complexities of ADU ownership and maximize your investment potential.
ADUs offer a flexible and innovative solution for today's savvy investors. They help you create additional rental income, make multi-generational living arrangements, and increase the value of your property.
FAQs
Q 1: What are ADUs in real estate?
A: ADUs, or Accessory Dwelling Units, are self-contained living spaces, attached or detached from a primary residence. They offer independent living space to occupants with amenities like a kitchen and bathroom.
Q 2: Do ADUs increase property taxes?
A: ADUs may impact your property taxes. However, the extent of this varies by location and local regulations.
Q 3: How many ADUs can I build on my property?
A: The number of ADUs allowed depends on your local zoning laws and property size.
Q 4: Are ADUs a good investment
A: ADUs can be a good investment, providing rental income, increased property value, and flexible living arrangements.
Q 5: Can I build 2 ADUs on my property,
A: Building multiple ADUs on one property is subject to local zoning laws and regulations. You may consult with a local authority or an ADU investment advisor for guidance.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always consult with a qualified financial professional before making investment decisions.




